High-Resolution Site Characterization Support in Mexico City
COLUMBIA Technologies is currently supporting our first high-resolution direct sensing project in...

COLUMBIA Technologies is currently supporting our first high-resolution direct sensing project in...

Article originally featured in the Environmental Business Journal (EBJ) Remediation & Redevelopment...

COLUMBIA Technologies has been recognized for their rapid expansion of their industry unique...
Article originally featured in the Probing Times, the official newsletter of Geoprobe Systems® Fall...

COLUMBIA Technologies’ state-of-the-art equipment and rapid 3D visualizations combined with...

Article originally featured in The Daily Record May 6, 2010 Issue One of the companies in the new...
Article originally featured in the Probing Times, the official newsletter of Geoprobe Systems® Fall...

Article originally featured in The Daily Record July 1, 2005 Issue A green company that saves...
COLUMBIA Technologies is currently supporting our first high-resolution direct sensing project in Mexico City. COLUMBIA’s direct sensing team landed in Mexico City in August to make a difference in the environmental industry on a global level and prove that real-time information can drive a project to satisfy regulatory requirements for investigation of contaminated sites.
Following the proven concept of stakeholder and regulatory involvement, systematic work planning, and dynamic work execution, these site investigations focused on providing a better understanding of how the results would impact the overall remediation scope and property disposition.
Tags: COLUMBIA Technologies, Direct Sensing, High Resolution Site Characterization (HRSC), John Sohl, Membrane Interface Probe (MIP), News, Mexico
Article originally featured in the Environmental Business Journal (EBJ) Remediation & Redevelopment Issue, Volume XXIV, Number 3/4, 2011
Throughout much of the approximately three-decade-old history of waste site cleanup, sub-surface site characterization has been something of a high-stakes gamble. You could install monitoring wells into the soil and groundwater, spending thousands of dollars per well while essentially guessing how best to develop a picture of where contamination has spread or where a groundwater plume is headed—and you could be wrong, prompting a costly revisiting of the site and possibly even lawsuits.
More recent history has seen the advent of high-resolution techniques that that have reduced the cost and improved the accuracy of sub-surface characterization. One company that has put those techniques to work at approximately 750 sites throughout its 10-year history is Columbia Technologies (Baltimore, MD), a provider of high-resolution direct sensing and mapping technologies such as the membrane interface probe (MIP), laser-induced fluorescence (LIF), the hydraulic profiling tool (HPT), a discrete groundwater profiler with on-site volatile organic compound (VOC) analysis, and associated data management tools for real-time information processing and visualization.
COLUMBIA Technologies CEO John Sohl looks back on the company’s experience at those 750 sites and sees three principles in play when it engages clients in today’s marketplace. First, “they want to define the issue, and not just produce data for data’s sake, and to keep regulators off their backs,” he says. Second, clients understand that better information leads to better decisions on cleanup and response. Third, “they’re saying, ‘I’d rather have an abundance of fairly close information and be approximately correct than be precisely wrong.’”
Tags: COLUMBIA Technologies, Hydraulic Profiling Tool (HPT), John Sohl, Membrane Interface Probe (MIP), News
COLUMBIA Technologies has been recognized for their rapid expansion of their industry unique business model throughout North America with EBJ’s 2010 Business Achievement Award for New Practice Areas. In 2010, COLUMBIA Technologies extrapolated their “on call” business model into 29 states including Hawaii, increasing their total market penetration to 45 of 50 states; and into the provinces of Alberta and Ontario, Canada. Upcoming projects are in the planning stage for Mexico as well as Puerto Rico.
In 2010, COLUMBIA Technologies worked with 57 different clients throughout North America and Hawaii at over 100 project locations. They contracted with 10 out of 20, 15 out of 30, and 20 out of 40 from the Environmental Business International’s top rated environmental consulting and engineering firms on a broad range of commercial and military sites.“Our unique business model enables us to work with environmental, legal and property professionals throughout the United States and overseas while delivering cost-effective solutions to optimize site remediation” said John Sohl, Chief Executive Officer for COLUMBIA Technologies. “In previous years and certainly in 2010, we’ve proven that COLUMBIA is not limited to a specific geographic region and our primary focus is serving our clients on a nationwide scale.”
Tags: COLUMBIA Technologies, John Sohl, News
Article originally featured in the Probing Times, the official newsletter of Geoprobe Systems® Fall 2010 Issue
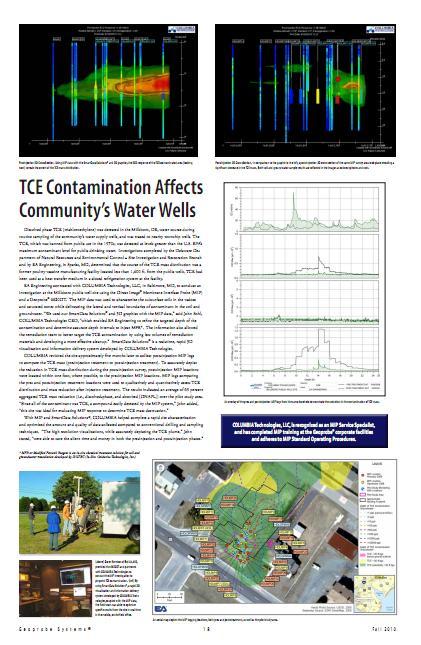
Dissolved phase TCE (trichloroethylene) was detected in the Millsboro, DE, water source during routine sampling of the community's water supply wells, and was traced to nearby township wells. The TCE, which was banned from public use in the 1970s, was detected at levels greater than the U.S. EPA's maximum contaminant level for public drinking water. Investigations completed by the Delaware Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Control – Site Investigation and Restoration Branch and by EA Engineering, in Sparks, MD, determined that the source of the TCE mass distribution was a former poultry vaccine manufacturing facility located less than 1,400 ft. from the public wells. TCE had been used as a heat transfer medium in a closed refrigeration system at the facility.
EA Engineering contracted with COLUMBIA Technologies, LLC, in Baltimore, MD, to conduct an investigation at the Millsboro public well site using the Direct Image® Membrane Interface Probe and a Geoprobe® 6620DT. The MIP data was used to characterize the subsurface soils in the vadose and saturated zones while delineating the lateral and vertical boundaries of contaminant in the soil and groundwater. "We used our SmartData Solutions® and 3D graphics with the MIP data," said John Sohl, COLUMBIA Technologies CEO, "which enabled EA Engineering to refine the targeted depth of the contamination and determine accurate depth intervals to inject MFR. The information also allowed the remediation team to better target the TCE contamination by using less volumes of remediation materials and developing a more effective cleanup." SmartData Solutions® is a real-time, rapid 3D visualizations and information delivery system developed by COLUMBIA Technologies.
Tags: COLUMBIA Technologies, News
COLUMBIA Technologies’ state-of-the-art equipment and rapid 3D visualizations combined with historical data completed a site assessment so efficiently that the original project work scope was reduced by 50%.
On this recently completed project, a major energy company required state clearance from regulators prior to advancing their expansion plans at an active petroleum refinery facility in western North Dakota.
Historical data indicated potential contamination in the expansion area requesting for rapid resolution to address regulatory concerns. The client engaged in a site assessment with COLUMBIA to map the area of concern and compare this with the historical data using COLUMBIA’s award winning SmartData Solutions®. With a dynamic work scope and real-time data measurement the team bound the area of concern and closed data gaps to reduce the problem at hand for the client as well as the regulatory agencies.
Tags: COLUMBIA Technologies, Laser Induced Fluorescence, LIF, LNAPL, News, SmartData Solutions®
Article originally featured in The Daily Record May 6, 2010 Issue
One of the companies in the new Maryland Clean Energy Incubator at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County is trying to make real estate development easier and faster.
Columbia Technologies, launched by two engineers in 1999, uses sensors to determine what kind of pollution is underneath a future or existing building site, turning weeks of waiting for an environmental analysis often needed in redevelopment projects into a few hours.
"We're able to get an answer quickly in high resolution that's easy to understand," said John H. Sohl, chief executive officer and co-founder of Columbia Technologies. "So you can move the market elements of a property transaction much faster."
The company's technology works by inserting a probe in the ground, sending data about the contaminants it detects in the soil to a computer. A three-dimensional, high-resolution image of the underground area covering about 50 feet is generated. Information on the underground contaminants is collected and used in the planning of the project.
"A developer is going to want to know how big and extensive the problem is and how much it's going to cost to bring it back to fruitful use," said Sohl, a former nuclear submarine captain.
Tags: COLUMBIA Technologies, John Sohl, News, SmartData Solutions®
Article originally featured in the Probing Times, the official newsletter of Geoprobe Systems® Fall 2009 Issue
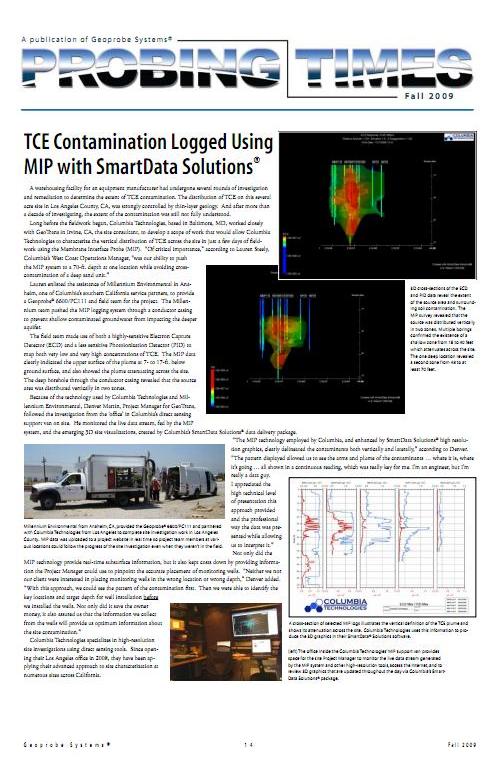
Long before the fieldwork began, Columbia Technologies, based in Baltimore, MD, worked closely with GeoTrans in Irvine, CA, the site consultant, to develop a scope of work that would allow Columbia Technologies to characterize the vertical distribution of TCE across the site in just a few days of fieldwork using the Membrane Interface Probe (MIP).
"Of critical importance," according to Lauren Steely, Columbia's West Coast Operations Manager, "was our ability to push the MIP system to a 70-ft. depth at one location while avoiding cross-contamination of a deep sand unit."
Lauren enlisted the assistance of Millennium Environmental in Anaheim, one of Columbia's southern California service partners, to provide a Geoprobe® 6600/PC111 and field team for the project. The Millennium team pushed the MIP logging system through a conductor casing to prevent shallow contaminated groundwater from impacting the deeper aquifer.
Tags: COLUMBIA Technologies, High Resolution Site Characterization (HRSC), Membrane Interface Probe, MIP, SmartData Solutions®
Article originally featured in The Daily Record July 1, 2005 Issue
"We have a broad appeal," said Ned Tillman, president and co-founder. "Environmental types like us for our less invasive procedures, but businesses like us because we can save them a lot of money. We're in a pretty good position."
The 6-year-old company has found a clean and fast way to measure subsurface pollution. While giving the environmentally concerned reason to cheer, Columbia is doing its share to keep commerce, particularly the real estate marketing, humming.
"Real estate transactions can close a lot faster now," Tillman said. "Before, a lot of deals would fall apart because of the time it would take to find out if there was contamination on a property. With our technology you can know that in a day."
The Catonsville-based company is now entering a growth phase. After spending its first three to four years engaged mostly in research and product development, the company has experienced "significant growth" over the past two years, according to Tillman. Business is expected to increase 15 to 20 percent annually for the next several years.
Columbia currently does about $2 million in annual revenue and is profitable, CEO and co-founder John Sohl said.
Tags: COLUMBIA Technologies, John Sohl, News, SmartData Solutions®
© COLUMBIA Technologies, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
HQ 1 Research Court Suite 450-402
Rockville, Maryland USA 20850-6252
Tel +1-888-344-2704 |
Email: info@columbiatechnologies.com
Privacy and Legal | Terms of Service